A steam power plant is one of the most widely used methods of generating electricity across the world. From small local grids to the biggest power plant in the world, the concept of producing power by converting water into high-pressure steam remains a cornerstone of modern energy production. In this detailed guide, we will explore the working principle, essential components, and an easy-to-understand diagram of a steam power plant. We will also look at the advantages and disadvantages of thermal power plants, the types of steam turbines, and how these plants operate in India and beyond.
What Is a Steam Power Plant?
A steam power plant, sometimes called a steam electric power station or steam generation plant, is a thermal power station where water is heated to produce steam. This high-pressure steam drives a steam turbine, which is mechanically connected to an electric generator. The rotation of the turbine converts thermal energy into mechanical and finally electrical energy.
In India, steam power plants contribute a large share of electricity production. Whether it is a small state facility or a mega installation like the NTPC stations, the power plant in India network relies heavily on the tried-and-tested steam generation process.
Also Read : Steam Power Generation Plant
Working Principle of a Steam Power Plant
The principle is straightforward but highly efficient:
- Fuel Combustion: Coal, natural gas, biomass, or oil is burned in a power plant boiler to create heat.
- Steam Generation: The heat converts water into high-temperature steam inside the boiler—hence the term steam generation.
- Turbine Operation: The pressurized steam expands and moves through the steam turbine, causing its blades to rotate.
- Electricity Generation: The turbine shaft is coupled to an alternator, producing electrical energy.
- Condensation & Recirculation: After passing through the turbine, the steam is cooled in a condenser and turned back into water to be reused.
This closed-loop cycle makes the steam electric power station efficient and economical.
Components of a Steam Power Plant
A modern steam power plant layout includes several critical components:
- Power Plant Boiler: The heart of the system where water is turned into steam.
- Superheater & Reheater: Increase the steam temperature for better turbine efficiency.
- Steam Turbine: Converts thermal energy of steam into mechanical energy. Various steam turbine types are used, such as impulse and reaction turbines.
- Condenser: Converts exhaust steam back to water for reuse.
- Cooling Tower: Removes excess heat from the system.
- Fuel Handling System: Manages the supply of coal or other fuels.
- Ash Handling System: Safely disposes of combustion residues.
- Generator: Produces electricity by electromagnetic induction.
Each of these elements must work in harmony to maintain consistent power generation.
Diagram of a Steam Power Plant
Understanding the steam power plant diagram helps visualize the process. A typical power plant diagram or layout of steam power plant shows:
Boiler at the starting point for heat generation
- Superheater and turbine in the middle stage
- Condenser and cooling tower for the final stage
Steam Power Plant Diagram
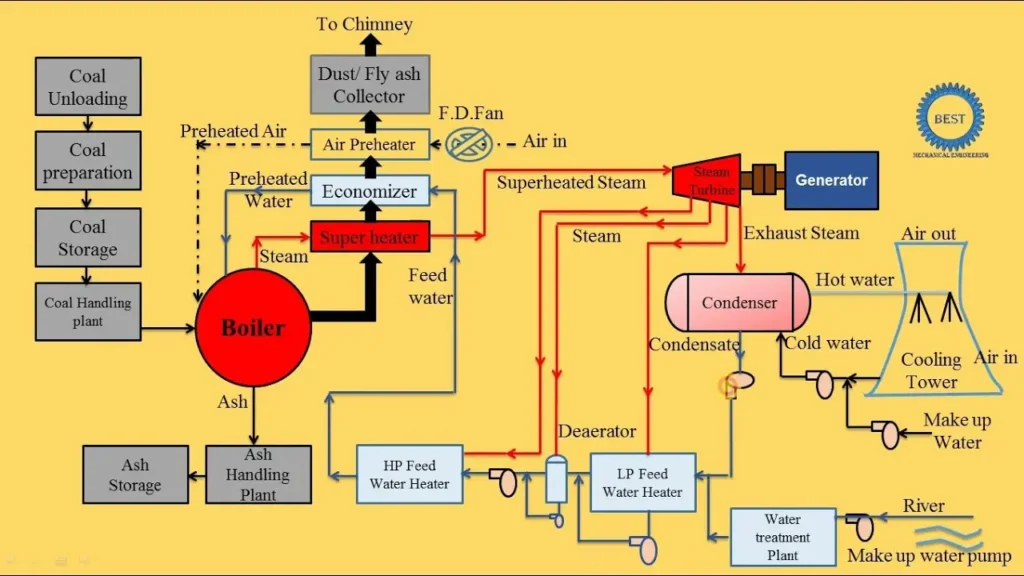
You may also encounter terms like steam plant diagram, steam generation plant diagram, or steam turbine diagram—all referring to slightly different illustrations of the same cycle.
Types of Steam Turbines
The steam turbines types used in power stations vary based on design and efficiency:
- Impulse Turbines – Steam hits the blades directly, causing rotation.
- Reaction Turbines – Steam expands through both fixed and moving blades, generating continuous motion.
Many modern stations combine these designs to maximize performance.
Advantages of Steam (Thermal) Power Plants
Steam electric power stations remain popular for several reasons:
- Abundant Fuel: Coal and natural gas are widely available.
- Stable Power Supply: Provides continuous base-load electricity.
- Scalability: Can be built to serve small towns or entire regions.
- Cost-Effective: Proven technology reduces setup costs compared to newer renewable systems.
These benefits explain why even in the era of solar and wind energy, the steam power plant remains a key energy source.
Disadvantages of Steam (Thermal) Power Plants
However, there are some notable advantages and disadvantages of thermal power plants to consider:
- Environmental Impact: Burning fossil fuels releases greenhouse gases.
- Water Usage: Large quantities of water are needed for cooling and steam production.
- High Maintenance: Boilers and turbines require regular upkeep.
- Fuel Price Fluctuation: Costs depend on global coal or gas prices.
Balancing these pros and cons is essential when planning new power projects.
Steam Power Plants in India
India is home to a vast network of thermal stations. From NTPC’s super thermal plants to regional facilities, the power plant in India infrastructure relies heavily on coal-based steam generation. Projects like Mundra and Vindhyachal rank among the largest in Asia, demonstrating how critical the layout of steam power plants is to the country’s electricity demand.
The Biggest Power Plant in the World
Globally, the title of biggest power plant in the world often goes to colossal hydroelectric stations like the Three Gorges Dam in China. However, among coal-based thermal plants, installations such as the Taichung Power Plant in Taiwan and the Kashima Plant in Japan represent the upper limits of steam power plant engineering. These plants showcase how far technology has come in scaling up steam generation for massive energy requirements.
Future of Steam Power Technology
While renewable energy is on the rise, research continues to make steam electric power stations cleaner and more efficient. Advanced power plant boilers, better steam turbine types, and carbon-capture technologies are being developed to reduce emissions and improve fuel efficiency. Hybrid systems combining biomass and coal also offer a promising path forward.
Conclusion
The steam power plant remains a fundamental technology for electricity production worldwide. By understanding its working principle, key components, and the diagram of a steam power plant, we gain insight into how much of our daily energy is generated. From the power plant in India network to the biggest power plant in the world, the process of steam generation continues to evolve.
Despite the advantages and disadvantages of thermal power plants, their reliability and scalability make them indispensable. As technology advances, we can expect cleaner, more efficient steam electric power stations to power industries and homes for decades to come.









