Thermal power plants are the most common and reliable method of electricity generation in the world. In this, heat is produced by burning fuel like coal, gas or oil, which turns water into steam and electricity is produced by running a turbine with that steam. Durga Boilers & Engineering Works has been providing high quality boilers and engineering solutions in this field for a long time. In this blog, we will learn in detail about the working of thermal power plants, its principles and thermal power plant diagrams.
Working of Thermal Power Plant
The working of thermal power plants takes place in several stages. First of all, fuel (coal, gas or oil) is burnt in the boiler, which generates heat energy. This heat turns the water present in the boiler into high pressure steam. This steam is transported to the turbine, where its pressure is used to rotate the turbine. The turbine is connected to the generator, which converts this mechanical energy into electrical energy. After this, the steam is cooled in the condenser and converted into water again and this water is sent back to the boiler, so that the cycle continues continuously.
Also Read : What Is the Difference Between Boiler Accessories And Boiler Mountings?
Principle of Thermal Power Plant
The principle of thermal power plants is based on the Rankine Cycle. According to this principle, heat energy is first converted into steam, then mechanical energy is obtained by running a turbine from that steam and finally this mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy through a generator. In this process, maximum use of heat energy is made and the system is designed in such a way that energy wastage is minimized.
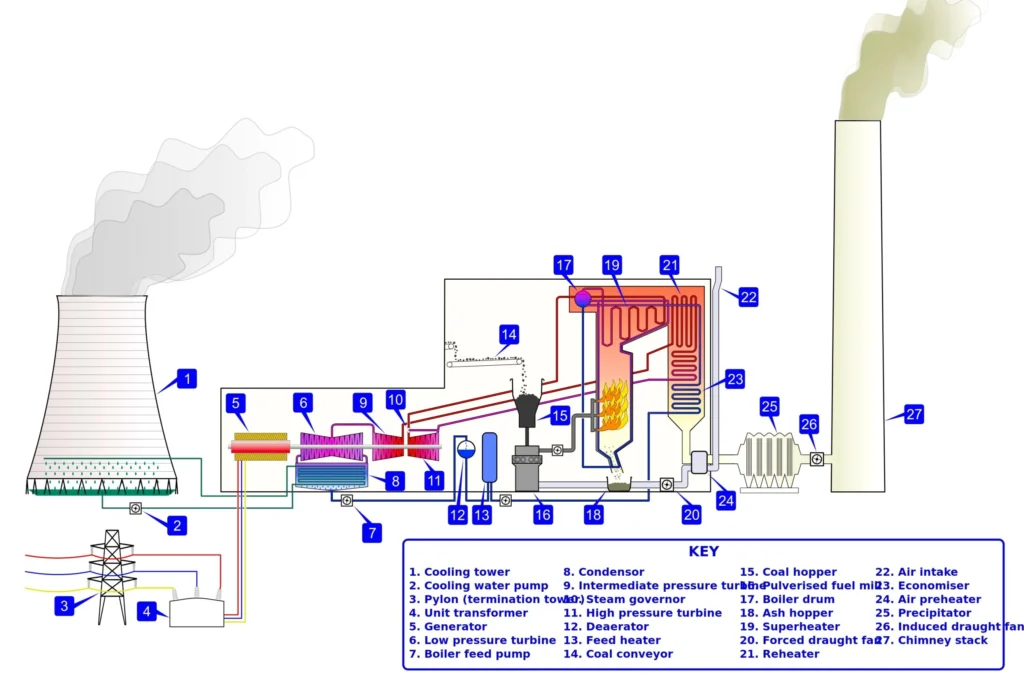
Thermal Power Plant Diagram
In a thermal power plant diagram, its main parts are clearly shown. In this, the boiler converts water into steam, the steam turbine rotates with this steam, the generator produces electricity from the speed of the turbine, the condenser cools the steam and converts it back into water, and the cooling tower maintains the circulation of cold water throughout the system. This diagram helps to explain the structure of the thermal power plant and its workflow in a simple way.
Diagram of Thermal Power Plant
Block Diagram of Thermal Power Plant
The block diagram of a thermal power plant is a simple but effective way to explain the entire system in steps. First the fuel is delivered to the boiler through the fuel system. In the boiler, the water is converted into steam and this steam rotates the turbine. The turbine is connected to the generator, which produces electricity. After this, the condenser cools the steam and turns it into water and the cooling water system maintains the entire plant at the right temperature.
Simple Thermal Power Plant Diagram
When we have to explain a simple structure, a simple thermal power plant diagram is used. It has four main parts – boiler, turbine, generator and condenser. Steam is produced in the boiler, the turbine rotates with that steam, the generator produces electricity and the condenser cools the steam and turns it into water. This simple form is ideal for beginner learners.
Advantages of Thermal Power Plant
The biggest advantage of a thermal power plant is that it can be run in any weather and at any time. It can also be installed where there is a water and fuel facility. It is excellent for base load power supply and is capable of generating electricity on a large scale. Apart from this, its operation and technology have been tried and reliable for a long time.
Disadvantages of Thermal Power Plant
However, it also has some disadvantages. It consumes more fuel and spreads pollution in the air, which has a negative impact on the environment. Also, there is a problem of disposal of ash and smoke. Its maintenance cost is also relatively high and water consumption is also high.
Applications of Thermal Power Plant
Thermal power plants are used to supply electricity in cities and villages. It is useful for large-scale power generation in industrial areas. Also, it is capable of meeting both peak load and base load power needs.
Conclusion
Understanding Thermal Power Plant: How does it Work, Principle & Diagram is important not only for engineering students but also for people working in the power industry. Thermal power plants are a trusted and long-used method of power generation. Durga Boilers & Engineering Works is known for its experience and high-quality solutions in this field and is making significant contributions to the power sector.










